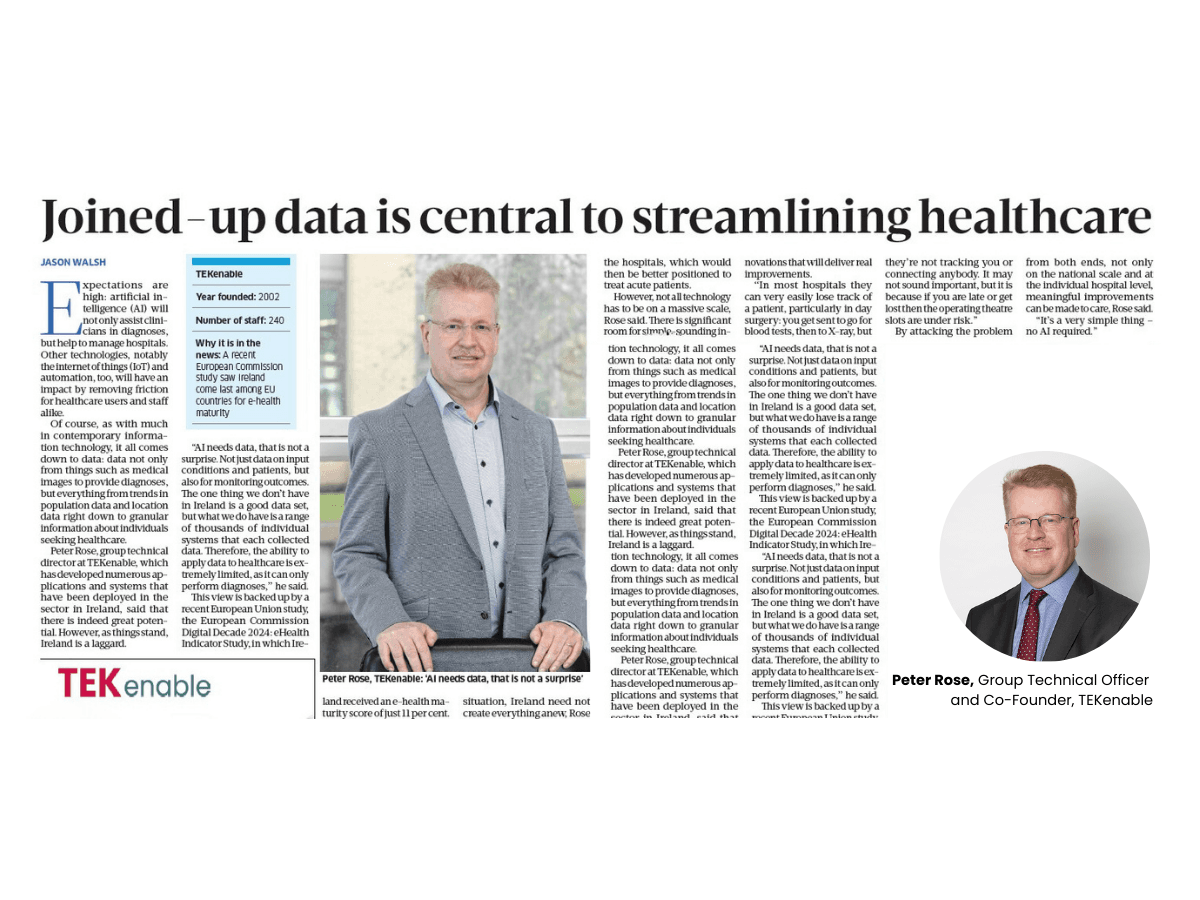
The software as a medical device market is expected to reach US$ 86,451.62 Million in 2027 from US$ 18,488.00 Million in 2019; it is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 21.9% from 2020 to 2027.
The global software as a medical device market is segmented by device type, application, deployment type, and geography. Based on device type, the market is segmented into PCs/laptops, smartphones/tablets, and wearable devices, and in 2019, the PCs/Laptops segment accounted for the largest market share.
The segment is expected to continue its dominance over the forecast period owing to the introduction of upgraded laptops with smart sensors incorporated in them. Furthermore, the laptops and computers are now being evolved into complex hardware systems that can act as an integrating tool as well as perform various monitoring and advance healthcare diagnostic activities through their new in-built features.
On the other hand, the growing adoption of smartphones and the interest of software developers toward building smartphones compatible healthcare apps to help it act as a medical device are expected to lead the smartphones/tablets segment toward the highest CAGR during the forecast period.
Medical devices including software, are regulated in the EU market by the EU Medical Device Regulations (MDR), and in the US Market by the FDA.
What is Software as a Medical Device?
The EU Medical Device Regulations (MDR) defines medical device as:
‘medical device’ means any instrument, apparatus, appliance, software, implant, reagent, material or other article intended by the manufacturer to be used, alone or in combination, for human beings, for one or more of the following specific medical purposes:
- diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, prediction, prognosis, treatment or alleviation of disease,
- diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, alleviation of, or compensation for, an injury or disability,
- investigation, replacement or modification of the anatomy or of a physiological or pathological process or state,
- providing information by means of in vitro examination of specimens derived from the human body, including organ, blood and tissue donations, and which does not achieve its principal intended action by pharmacological, immunological or metabolic means, in or on the human body, but which may be assisted in its function by such means.
In effect any software which aids in the diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, prognosis treatment or alleviation of disease is classified as a SaMD under MDR. This is all dependent on the manufacturers definition of the intended use of the product.
What are the EU Medical Device Regulations (MDR)?
The new Medical Devices Regulation (2017/745/EU) (MDR) and the In-vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices Regulation (2017/746/EU) (IVDR) bring EU legislation into line with technical advances, changes in medical science, and progress in law making.
Regulation 2017/745 on Medical Devices (MDR) and Regulation 2017/746 on In-Vitro Diagnostic Devices (IVDR) were agreed at a political level between the three relevant European institutions (the European Council, the European Parliament and the European Commission) and entered into force in May 2017 following publication in the Official Journal of the European Union. The Regulations have a staggered transitional period with some aspects becoming legally binding after 6 months of entry into force.
The MDR was due to become fully applicable on 26 May 2020 after a three-year transition period. However, due to the global outbreak of Covid-19, full application of the MDR has been postponed and will become fully applicable on 26 May 2021. The IVDR will be fully applicable on 26 May 2022, after a five-year transition period.
Medical software that falls under the scope of the MDR is considered a medical device and needs CE marking.
Who is a manufacturer?
Definition of a manufacturer: means a natural or legal person who manufactures or fully refurbishes a device or has a device designed, manufactured or fully refurbished, and markets that device under its name or trade name.
Obligation on manufacturers?
The obligations of the different actors and their relations are now clearly stated in the Regulation.
The manufacturers must document the intended use
According to Article 10, manufacturers shall have systems for risk management (paragraph 2) and quality management (paragraph 9); conduct clinical evaluations (paragraph 3); compile technical documentation (paragraph 4); and apply a conformity assessment procedure (paragraph 6). Manufacturers are also responsible for their devices once they are on the market (paragraphs 12, 13, 14). They must have systems in place to cover their financial responsibility for harm caused by defective devices (paragraph 16).
Every manufacturer shall have a named person responsible for regulatory compliance (Article 15).
Once they have completed all these obligations, manufacturers shall draw up a declaration of conformity (Article 19) and apply CE marking to their devices (Article 20).
Manufacturers outside the EU/EEA shall have a contract with an authorised representative inside the EU/EEA4 (Article 11).
Classification of Medical devices.
A new rigid, software-specific classification rule pushes devices into the higher risk classes II or III (Rule 11). To date, software as a medical device (SaMD) has often been classified as a class I product. Under the MDR, this will change drastically. Almost all software as a medical device will be up-classified into higher risk classes.
Rule 11 (MDR):
Software intended to provide information which is used to take decisions with diagnosis or therapeutic purposes is classified as class IIa, except if such decisions have an impact that may cause:
- death or an irreversible deterioration of a person’s state of health, in which case it is in class III; or
- a serious deterioration of a person’s state of health or a surgical intervention, in which case it is classified as class IIb.
Software intended to monitor physiological processes is classified as class IIa, except if it is intended for monitoring of vital physiological parameters, where the nature of variations of those parameters is such that it could result in immediate danger to the patient, in which case it is classified as class IIb.
All other software is classified as class I.
*Class 1 is effectively impossible under MDR, as the definition for 2a includes “used for treatment or diagnosis” which is the same criteria to qualify as a SaMD.
Impact of MDR on QMS
All medical devices, whether currently certified to a European Medical Directive or yet to be certified, will need to comply with the requirements of the MDR to be certified under the MDR. The MDR requires manufacturers to demonstrate an effective QMS. Therefore, to receive certification to the MDR, you must have a compliant QMS within the transition period, as set out in Article 120.
While MDR is not specific on what certified and audited QMS is in place, in effect ISO13485 is the only current QMS available that can be certified at present.
Class II or III: Medical device manufacturers need to get their CE marking approved by a Notified Body (NB). Instead of self-assessment, the NB assesses the device conformity and approves the CE marking with the NB-specific 4-digit identification number.
Can a manufacturer outsource Software Development?
Yes, outsourcing to a software development company certified to ISO13485 is possible, and software and documentation generated during development can be imported into the manufacturers own QMS and technical file. Third parties do not take on the manufacturers legal responsibilities, however their systems and processes under ISO13485 may also be audited on behalf of the manufacturer.
Greenfinch Technology, part of the TEKenable Group is a Dublin based company, providing healthcare software development services for creating medical apps classified as Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) under the medical device regulations. Our team brings a wealth of experience in using the Microsoft technology stack and other technologies. We use the IEC 62304 software development process, helping to deliver software applications conforming to ISO 13485 regulations. Greenfinch Technology is an Irish software development company that specialises in SaMD projects.